“New year, new me!”
The dawn of a new year sees many of you making plans to change your health for the better. The aftermath of overindulgence combined with a good amount of rest and the promise of a fresh new calendar gives us the motivation to be better. This quest to uncover the improved version of yourself often involves some kind of “detox” but what does that mean and where do you even start? We’ve put together some tips on how to detox and why you should want to.
What is detoxification?
Detoxification is a process that happens every single day as your liver, kidneys and even skin are constantly getting rid of detrimental compounds. Toxins (defined as any compounds that have a detrimental effect on cell function or structure) come from everywhere – the air we breathe, the food we eat and the water we drink. Your body and the microbes that live in it produce “toxins” as part of everyday metabolism as well, however, the amount of toxins produced increase when we overindulge.
And let’s be honest, that’s what often happens in the holidays… we eat more unhealthy foods, drink more alcohol, and potentially take more painkillers to deal with the subsequent hangovers.
Toxins only become a worry if the amount of toxins exceeds the amount that your detoxification pathways can safely deal with. If this happens, toxins build up in the body and you may become trapped in a negative cycle where excess toxins overburden the organs that are involved in the detoxification process.
Signs you might need detoxification products
If you experience any of the following, you might need to give your detoxification pathways a helping hand include:
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Bloating and indigestion
- Brain fog
- Weight gain
- Dermatitis (inflammation on the skin)
- Recent heavy alcohol use
- Recent overindulgence
Complimentary medicines may assist in neutralizing and excreting toxins when in overload, clearing the backlog and paving the way for a ‘cleaner’ system. At the same time, it is important to reduce the workload for your detox organs by eating a diet rich in wholefoods, fruits, vegetables and drinking plenty of pure water. Avoiding junk food, sugar, and alcohol is also super important!
Detox supplements
Phytoceutics™️ have scoured the world to find premium quality nutraceuticals that are produced by nature, supported by science and assist in optimising your health. If you’re wondering how to detox, this portfolio includes three powerful detoxification products designed to support your body through the process of detoxification. These include:
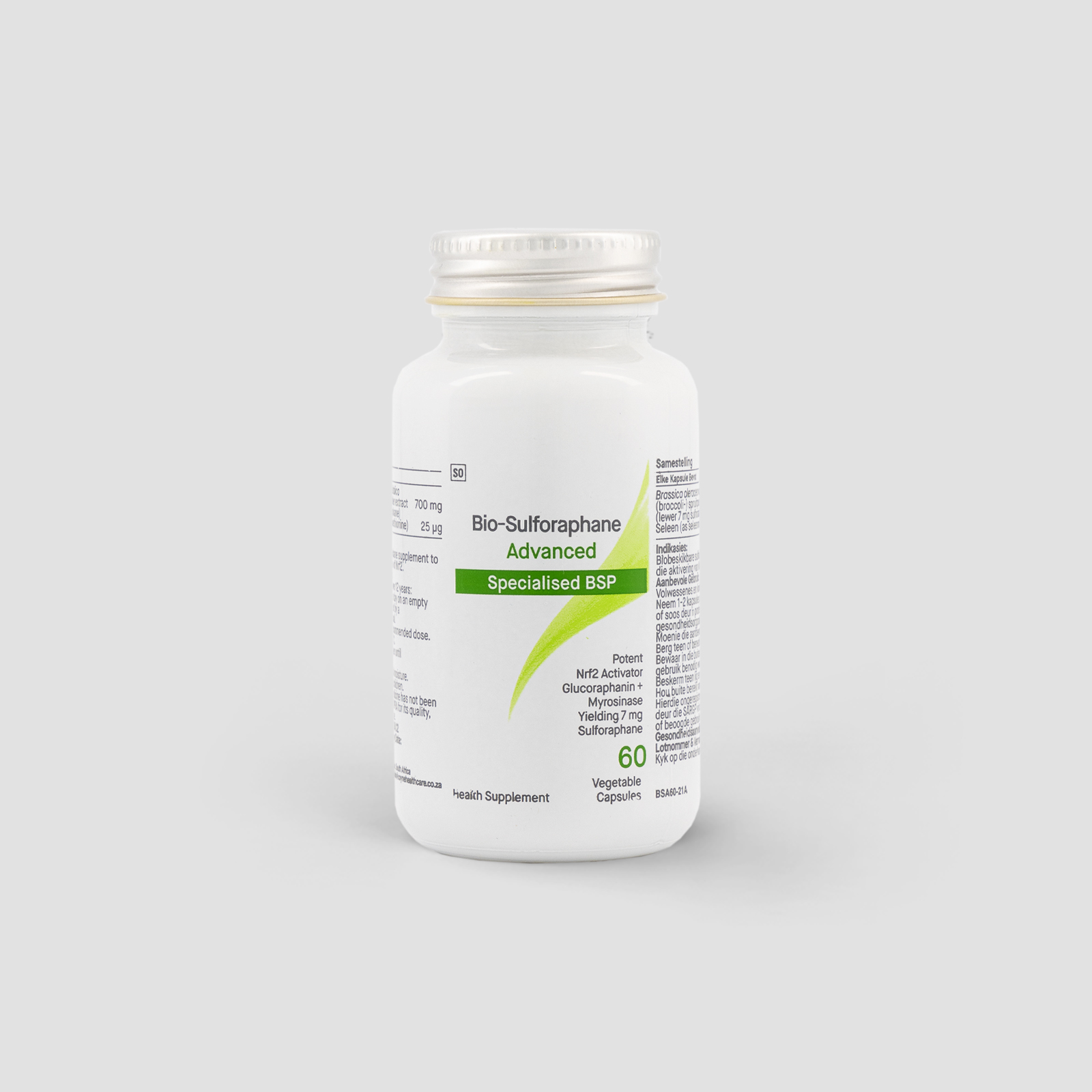
Bio-Sulforaphane Advanced is a highly bioavailable concentrated source of broccoli sprout phytonutrients, which assist in regulating the work of antioxidant proteins that can help protect against free radicals (which cause oxidative stress) and promote detoxification. Oxidative stress can damage cells, proteins, and DNA, which can contribute to numerous health conditions.
By harnessing the power of your own cellular machinery, sulforaphane assists your genetics to support detoxification via multiple pathways. Furthermore, sulforaphane activates a genetic switch called NRF-2 which, when switched on, increases a large variety of detoxification enzymes and antioxidants (Ruhee & Suzuki, 2020).
Milk thistle is likely one of the most well-known herbs out there when it comes to liver health and detoxification. Milk thistle seed contains a potent combination of antioxidants known as silymarin, with silibyn being the most potent and abundant antioxidant compound within this group (Surai, 2015).
Bio-Milk Thistle is unique in that it provides both a certified organic “full spectrum” milk thistle extract that is standardized to contain at least 80% silymarin, and a specialized extract of silybin in a phosphatidylcholine sphere which enhances the absorption of the silybin when compared to regular milk thistle extracts (Kidd & Head, 2005).
The phosphatidylcholine in this formulation also helps to further protect liver cells and enhance liver function (Maev, et. al. 2020).
Glutathione is often referred to as the master antioxidant, as it helps the body detoxify in many different ways. Not only can it help the cells in your body excrete toxins, but it can also help neutralize different toxins (Pizzorno, 2014).
In the past it was difficult to increase glutathione levels with oral supplementation because it would simply be broken down into the three amino acid building blocks that it is made from in the gut. However, Biomax Glutathione contains a specific form of glutathione called Setria®, which is proven to overcome this malabsorption and increase cellular levels (Richie, et al. 2015). Liposomal encapsulation further enhances the bioavailability of this special form of glutathione with the added benefit of the phosphatidylcholine protecting liver cells and enhancing liver function.
Find out more about your supplements for detoxification.